India and China's - Game of Thrones via Economic and Political Lens
Indias Conundrum
India is playing its part in the BRICS because of the following
India's trust in China has eroded due to 4 skirmishes at the Northern Border. India is wary of China's growing clout in the new world order. While BRICS is economically China-centric, it is ensuring that it doesn't become a Unipolar bloc in Asia and another India-bashing group like OIC used to be. India can no longer rely on Russia as it has been forced to become China's ally because of sanctions.
By consenting to an expansion, it is mounting pressure on China and other relevant parties to acknowledge its deserving position in the UN's Permanent Five + Group and refrain from raising objections.
Besides India's trade deficit with the New BRICS being around 69%, prompting a need for effective management. In response, India is seeking to promote the use of local currency in trade transactions, thereby reducing its reliance on the USD and conserving Forex reserves. Furthermore, UAE has agreed to do business in Indian Rs, a significant development in this regard.
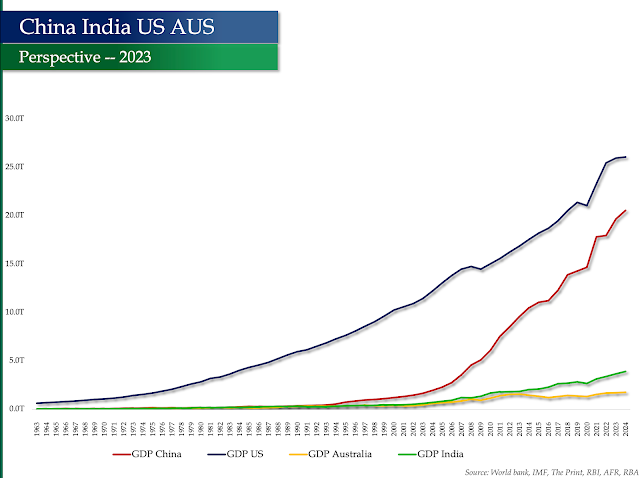
In light of the ongoing conflict in Ukraine and the economic impacts of COVID-19, the New BRICS bloc, which now includes Argentina, Iran, Ethiopia, Egypt, UAE, and Saudi Arabia, is expected to have a combined GDP of $29.14 Tn. The New BRICS bloc has a population of 3.6 Bn, which accounts for 51.6% of the world's population, while G7 has a population of only 0.8 Bn, which accounts for only 10.9% of the world's population.
--
Why China Wants to Invade Taiwan
- China has been threatening to invade Taiwan, claiming it as part of its One China policy due to cultural and historical reasons.
- Being a highly authoritarian country with minimal democratic values, it cannot afford to have an island nation located merely 150 kilometers away from its mainland that practices democracy.
- Taiwan holds a prominent position as the global leader in the semiconductor industry, with TSMC as its flagship company. Today Semiconductors are crucial components in the defense, space, and technology sectors.
- China's trade deficit is exacerbated by its reliance on Taiwan for advanced semiconductors, prompting it to seek industry dominance and supply chain control.
- The US, which has a $400Bn trade deficit with China, is preventing China from acquiring advanced semiconductor technology, fuelling further tension. Therefore, China has multiple reasons to invade, including cultural, political, and economic factors.
- Analysts argue that the US is feeling the pressure because they facilitated China's ascent as a manufacturing hub and are now seeking to diversify supply chains to mitigate risks in the post-COVID era.
- China's trade deficit with Australia is being driven by continued demand for its resources, while Australia post-COVID, is diversifying its import and export portfolio.













 A single chip can cost upwards of US$40K, and OpenAI used about 10,000 of them to train ChatGPT. If you want to train a GPT5-level model, you apparently need somewhere on the order of 20K to 25K H100 GPU accelerators, and that is somewhere around two dozen $1 billion machines
A single chip can cost upwards of US$40K, and OpenAI used about 10,000 of them to train ChatGPT. If you want to train a GPT5-level model, you apparently need somewhere on the order of 20K to 25K H100 GPU accelerators, and that is somewhere around two dozen $1 billion machines