Featured Post
The Great Pricing Shift: How AI Is Breaking Traditional Revenue Models
------ 1. The Great Pricing Shift We're witnessing something unprecedented in business history: a fundamental reimagining of how comp...
Wednesday, August 28, 2024
From Four to Six Pillars: The Evolution of the Australian Telecom Industry
Monday, August 12, 2024
Nvidia's Post-Earnings Boost is Ahead: A Breakdown
Nvidia's Post-Earnings Boost: A Breakdown
Nvidia's upcoming earnings call on August 28th is highly anticipated due to several key factors that position the company for a potential share price surge.
Key Factors Driving Nvidia's Potential Post-Earnings Boost
-
Inventory Disparity:
- Nvidia's low inventory levels compared to AMD's bloated stock suggest strong demand and efficient production. This indicates a healthier financial position and potential for higher revenue.
- The contrast between the two chip giants highlights Nvidia's superior supply chain management and ability to capitalize on market demand.
-
Dominant Pricing Power:
- Nvidia's H100 GPUs command a significantly higher price than AMD's competing MI300X, demonstrating exceptional pricing power.
- This pricing advantage translates into higher revenue per unit and improved profit margins, contributing to overall financial strength.
-
LLM-Driven Demand Acceleration:
- The burgeoning LLM market is a key growth driver for Nvidia, as these models require immense computational power provided by its high-performance GPUs.
- The rapid expansion of LLM model sizes and training requirements indicates sustained demand for Nvidia's chips in the foreseeable future.
-
Outperforming AMD in Data Center Segment:
- While AMD reported impressive growth in its data centre segment, Nvidia's superior inventory management and pricing power position it to potentially deliver even stronger results.
- This outperformance could further solidify Nvidia's dominance in the AI chip market.
-
Valuation and Volatility:
- Despite its high valuation, Nvidia's stock is characterized by significant volatility.
- Positive earnings results could trigger a substantial upward movement in the share price, given the high investor interest in the company.
The Broader Tech Landscape: A Comparative Analysis
When compared to other tech giants, Nvidia stands out in terms of its focus on AI and high-performance computing. Companies like Amazon, Meta, Microsoft, and Google are investing heavily in AI infrastructure, as evidenced by their high CapEx to Operating Cash Flow ratios. Apple, on the other hand, appears to be taking a more cautious approach.
Nvidia's role as a critical supplier of AI hardware positions it as a key beneficiary of this industry-wide trend. Its ability to convert this demand into strong financial performance will be a key focus for investors during the earnings call.
In conclusion, the combination of low inventory, high pricing power, and the booming LLM market creates a compelling case for Nvidia's post-earnings share price appreciation. While the stock's valuation and market volatility introduce risks, the company's strong competitive position and the overall positive industry outlook make it a compelling investment opportunity.
Image Credit: Richad Jarc.
Thursday, July 25, 2024
Book - Gen AI The New Reality - How Key Players Are Progressing
Gen AI The New Reality - How Key Players Are Progressing
About the BookEmbark on a journey through the world of chipmakers, where TSMC reigns supreme, pioneering the most advanced chips, yet facing its unique challenges. Discover the driving forces behind Nvidia's dominance as the "Godfather of AI" and analyse the potential for a dot-com bubble resurgence.
Venture into the realm of Hyperscalers, where Microsoft stands as the undisputed king of AI in the cloud and software. Explore its strategic partnerships, the economics of training AI systems, and the inherent risks associated with its growth.
Delve into the world of Google, the search giant that's leveraging Gen AI to revolutionize its offerings. Examine its search economics, cloud play, diversification efforts, and the infamous $100 billion blunder.
Uncover the secrets behind Amazon's retail empire, where multiple flywheels drive its growth. Analyse the intricacies of AWS, the crown jewel of Amazon's offerings, and the company's pursuit of new flywheels.
Step into the automotive sector, where Tesla stands as a visionary leader, constantly reinventing its vehicles. Explore the company's secret sauce, its growth trajectory, its ambitious FSD plans, and the role of AI-enabled Dojo.
Discover how Oracle, the database leader, is transforming into an AI innovator. Understand the company's growth strategy, its focus on Gen AI, and the challenges it faces.
Dive into the world of Salesforce, a cloud and AI-powered CRM giant. Explore its growth trajectory, its evolving relationship with competitors, and the potential risks it faces.
Examine SAP, the ERP market leader, as it strives to become a one-stop shop for businesses. Understand the company's efforts to catch up with AI advancements and the challenges it faces.
Uncover the story of IBM, a tech giant facing growth hurdles. Analyse its history of misfires, its comprehensive AI play, and the factors that have led to its relative stagnation in recent years.
- Understand the evolution, hype, and potential of Generative AI.
- Discover the value chain, deployment models, and future growth of LLMs.
- Analyse the dominance of chipmakers like TSMC and Nvidia.
- Delve into the AI strategies of Hyperscalers like Microsoft, Google, and Amazon.
- Explore the AI innovations of automotive, software, and security companies.
- This book provides a comprehensive overview of the Generative AI landscape, equipping readers with the insights needed to navigate this transformative era.
The sample chapters on Hyperscalers and Chip Makers are available for download below.
Monday, June 03, 2024
The Future of Software is New SaaS
The Future of Software is New SaaS - powered by Services, AI Agents, Sharing
Wednesday, March 27, 2024
Aussie BroadBand on Acquisition Spree
First, what I wrote about ABB's FY23 Results last year.
Update on ABB's Business
ABB's Acquisition Spree - Ongoing Tussle and Drivers Behind it.
Tuesday, March 26, 2024
Australias Telecom Industry in Transition
Australia Telecom Industry in Transition - From Four Pillar to Six Pillar Model
Australia Telecom Industry - Fixed Internet Ranking
My previous post on the Global Telecom Industry Evolution to date.
Tuesday, October 17, 2023
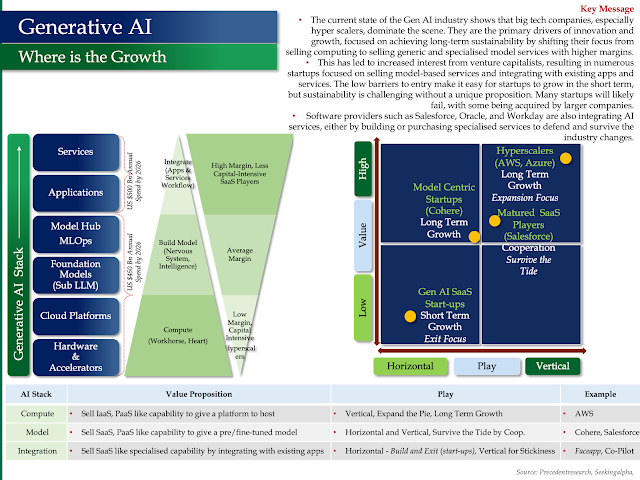
Generative AI - Where is The Growth ?
Generative AI - Where is The Growth?
- The current state of the Gen AI industry shows that big tech companies, especially hyper scalers, dominate the scene. They are the primary drivers of innovation and growth, focused on achieving long-term sustainability by shifting their focus from selling computing to selling generic and specialised model services with higher margins.
- This has led to increased interest from venture capitalists, resulting in numerous startups focused on selling model-based services and integrating with existing apps and services. The low barriers to entry make it easy for startups to grow in the short term, but sustainability is challenging without a unique proposition. Many startups will likely fail, with some being acquired by larger companies.
- Software providers such as Salesforce, Oracle, and Workday are also integrating AI services, either by building or purchasing specialised services to defend and survive the industry changes.
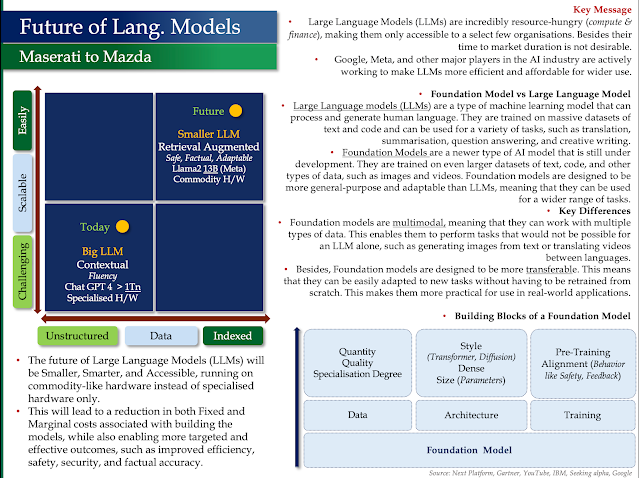
Future of Language Models
- Large Language Models (LLMs) are incredibly resource-hungry (compute & finance), making them only accessible to a select few organisations. Besides their time to market duration is not desirable.
- Google, Meta, and other major players in the AI industry are actively working to make LLMs more efficient and affordable for wider
Foundation Model vs Large Language Model
Large Language models (LLMs) are a type of machine learning model that can process and generate human language. They are trained on massive datasets of text and code and can be used for a variety of tasks, such as translation, summarisation, question answering, and creative writing.
Foundation Models are a newer type of AI model that is still under development. They are trained on even larger datasets of text, code, and other types of data, such as images and videos. Foundation models are designed to be more general-purpose and adaptable than LLMs, meaning that they can be used for a wider range of tasks.
Key Differences
Foundation models are multimodal, meaning that they can work with multiple types of data. This enables them to perform tasks that would not be possible for an LLM alone, such as generating images from text or translating videos between languages.
Besides, Foundation models are designed to be more transferable. This means that they can be easily adapted to new tasks without having to be retrained from scratch. This makes them more practical for use in real-world applications.
My other posts on Generative AI and Strategic Analysis of Key Players
- AI Value Chain
- Amazon the King of Retail -WhyAWS is the Crown Jewel
- Microsoft the King of AI in Software, Salesforce under the AI Cloud
- Tesla - It's not a Car, It's an AI Device on Wheels
- Google the King of Search - What the Future Beholds in the AI World
- Nvidia Godfather of AI - Why the Market is Bullish
- IBM - How it Lost Its Way
- Generative AI can transform Telecoms, Energy and Utilities