Featured Post
The Great Pricing Shift: How AI Is Breaking Traditional Revenue Models
------ 1. The Great Pricing Shift We're witnessing something unprecedented in business history: a fundamental reimagining of how comp...
Wednesday, August 28, 2024
From Four to Six Pillars: The Evolution of the Australian Telecom Industry
Monday, August 12, 2024
Nvidia's Post-Earnings Boost is Ahead: A Breakdown
Nvidia's Post-Earnings Boost: A Breakdown
Nvidia's upcoming earnings call on August 28th is highly anticipated due to several key factors that position the company for a potential share price surge.
Key Factors Driving Nvidia's Potential Post-Earnings Boost
-
Inventory Disparity:
- Nvidia's low inventory levels compared to AMD's bloated stock suggest strong demand and efficient production. This indicates a healthier financial position and potential for higher revenue.
- The contrast between the two chip giants highlights Nvidia's superior supply chain management and ability to capitalize on market demand.
-
Dominant Pricing Power:
- Nvidia's H100 GPUs command a significantly higher price than AMD's competing MI300X, demonstrating exceptional pricing power.
- This pricing advantage translates into higher revenue per unit and improved profit margins, contributing to overall financial strength.
-
LLM-Driven Demand Acceleration:
- The burgeoning LLM market is a key growth driver for Nvidia, as these models require immense computational power provided by its high-performance GPUs.
- The rapid expansion of LLM model sizes and training requirements indicates sustained demand for Nvidia's chips in the foreseeable future.
-
Outperforming AMD in Data Center Segment:
- While AMD reported impressive growth in its data centre segment, Nvidia's superior inventory management and pricing power position it to potentially deliver even stronger results.
- This outperformance could further solidify Nvidia's dominance in the AI chip market.
-
Valuation and Volatility:
- Despite its high valuation, Nvidia's stock is characterized by significant volatility.
- Positive earnings results could trigger a substantial upward movement in the share price, given the high investor interest in the company.
The Broader Tech Landscape: A Comparative Analysis
When compared to other tech giants, Nvidia stands out in terms of its focus on AI and high-performance computing. Companies like Amazon, Meta, Microsoft, and Google are investing heavily in AI infrastructure, as evidenced by their high CapEx to Operating Cash Flow ratios. Apple, on the other hand, appears to be taking a more cautious approach.
Nvidia's role as a critical supplier of AI hardware positions it as a key beneficiary of this industry-wide trend. Its ability to convert this demand into strong financial performance will be a key focus for investors during the earnings call.
In conclusion, the combination of low inventory, high pricing power, and the booming LLM market creates a compelling case for Nvidia's post-earnings share price appreciation. While the stock's valuation and market volatility introduce risks, the company's strong competitive position and the overall positive industry outlook make it a compelling investment opportunity.
Image Credit: Richad Jarc.
Thursday, July 25, 2024
Book - Gen AI The New Reality - How Key Players Are Progressing
Gen AI The New Reality - How Key Players Are Progressing
About the BookEmbark on a journey through the world of chipmakers, where TSMC reigns supreme, pioneering the most advanced chips, yet facing its unique challenges. Discover the driving forces behind Nvidia's dominance as the "Godfather of AI" and analyse the potential for a dot-com bubble resurgence.
Venture into the realm of Hyperscalers, where Microsoft stands as the undisputed king of AI in the cloud and software. Explore its strategic partnerships, the economics of training AI systems, and the inherent risks associated with its growth.
Delve into the world of Google, the search giant that's leveraging Gen AI to revolutionize its offerings. Examine its search economics, cloud play, diversification efforts, and the infamous $100 billion blunder.
Uncover the secrets behind Amazon's retail empire, where multiple flywheels drive its growth. Analyse the intricacies of AWS, the crown jewel of Amazon's offerings, and the company's pursuit of new flywheels.
Step into the automotive sector, where Tesla stands as a visionary leader, constantly reinventing its vehicles. Explore the company's secret sauce, its growth trajectory, its ambitious FSD plans, and the role of AI-enabled Dojo.
Discover how Oracle, the database leader, is transforming into an AI innovator. Understand the company's growth strategy, its focus on Gen AI, and the challenges it faces.
Dive into the world of Salesforce, a cloud and AI-powered CRM giant. Explore its growth trajectory, its evolving relationship with competitors, and the potential risks it faces.
Examine SAP, the ERP market leader, as it strives to become a one-stop shop for businesses. Understand the company's efforts to catch up with AI advancements and the challenges it faces.
Uncover the story of IBM, a tech giant facing growth hurdles. Analyse its history of misfires, its comprehensive AI play, and the factors that have led to its relative stagnation in recent years.
- Understand the evolution, hype, and potential of Generative AI.
- Discover the value chain, deployment models, and future growth of LLMs.
- Analyse the dominance of chipmakers like TSMC and Nvidia.
- Delve into the AI strategies of Hyperscalers like Microsoft, Google, and Amazon.
- Explore the AI innovations of automotive, software, and security companies.
- This book provides a comprehensive overview of the Generative AI landscape, equipping readers with the insights needed to navigate this transformative era.
The sample chapters on Hyperscalers and Chip Makers are available for download below.
Monday, June 03, 2024
The Future of Software is New SaaS
The Future of Software is New SaaS - powered by Services, AI Agents, Sharing
Wednesday, March 27, 2024
Aussie BroadBand on Acquisition Spree
First, what I wrote about ABB's FY23 Results last year.
Update on ABB's Business
ABB's Acquisition Spree - Ongoing Tussle and Drivers Behind it.
Tuesday, March 26, 2024
Australias Telecom Industry in Transition
Australia Telecom Industry in Transition - From Four Pillar to Six Pillar Model
Australia Telecom Industry - Fixed Internet Ranking
My previous post on the Global Telecom Industry Evolution to date.
Tuesday, October 17, 2023
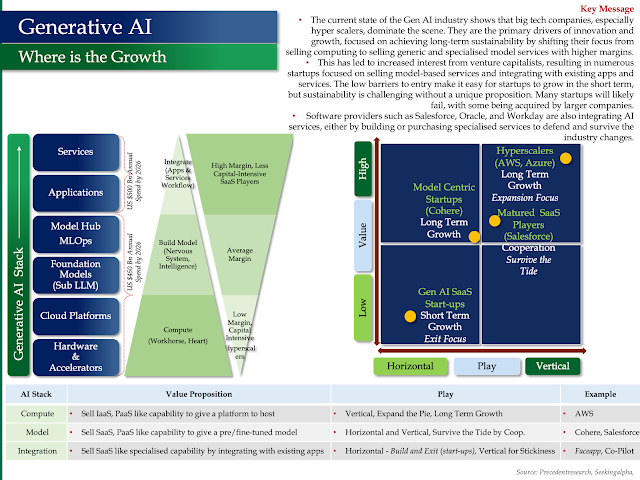
Generative AI - Where is The Growth ?
Generative AI - Where is The Growth?
- The current state of the Gen AI industry shows that big tech companies, especially hyper scalers, dominate the scene. They are the primary drivers of innovation and growth, focused on achieving long-term sustainability by shifting their focus from selling computing to selling generic and specialised model services with higher margins.
- This has led to increased interest from venture capitalists, resulting in numerous startups focused on selling model-based services and integrating with existing apps and services. The low barriers to entry make it easy for startups to grow in the short term, but sustainability is challenging without a unique proposition. Many startups will likely fail, with some being acquired by larger companies.
- Software providers such as Salesforce, Oracle, and Workday are also integrating AI services, either by building or purchasing specialised services to defend and survive the industry changes.
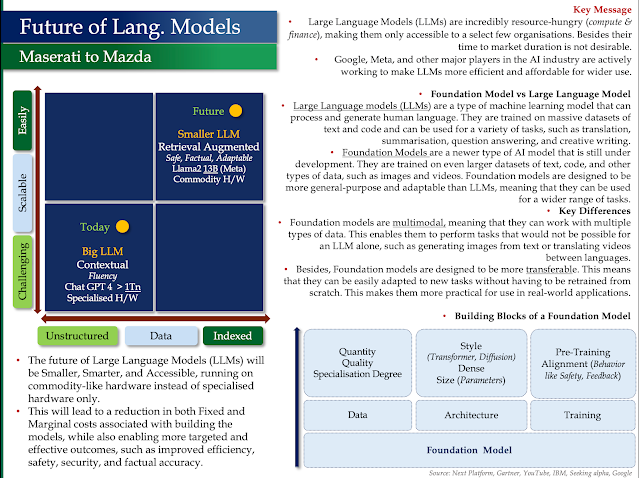
Future of Language Models
- Large Language Models (LLMs) are incredibly resource-hungry (compute & finance), making them only accessible to a select few organisations. Besides their time to market duration is not desirable.
- Google, Meta, and other major players in the AI industry are actively working to make LLMs more efficient and affordable for wider
Foundation Model vs Large Language Model
Large Language models (LLMs) are a type of machine learning model that can process and generate human language. They are trained on massive datasets of text and code and can be used for a variety of tasks, such as translation, summarisation, question answering, and creative writing.
Foundation Models are a newer type of AI model that is still under development. They are trained on even larger datasets of text, code, and other types of data, such as images and videos. Foundation models are designed to be more general-purpose and adaptable than LLMs, meaning that they can be used for a wider range of tasks.
Key Differences
Foundation models are multimodal, meaning that they can work with multiple types of data. This enables them to perform tasks that would not be possible for an LLM alone, such as generating images from text or translating videos between languages.
Besides, Foundation models are designed to be more transferable. This means that they can be easily adapted to new tasks without having to be retrained from scratch. This makes them more practical for use in real-world applications.
My other posts on Generative AI and Strategic Analysis of Key Players
- AI Value Chain
- Amazon the King of Retail -WhyAWS is the Crown Jewel
- Microsoft the King of AI in Software, Salesforce under the AI Cloud
- Tesla - It's not a Car, It's an AI Device on Wheels
- Google the King of Search - What the Future Beholds in the AI World
- Nvidia Godfather of AI - Why the Market is Bullish
- IBM - How it Lost Its Way
- Generative AI can transform Telecoms, Energy and Utilities
Friday, October 06, 2023
Generative AI - Framework to Identify Use Case and Investment
Generative AI - Framework to Identify Use Case and Investment
Tuesday, October 03, 2023
Palo Alto Networks - What is their Growth Template
Palo Alto Networks - Leader in Cyber Security
Key Indicators
- Market Cap – 73.07 Bn
- EV – 72.95 Bn
- Debt - $2.26Bn
- P/B – 41.79 (Goodwill from M&A)
- P/E (Trailing) – 184.99 (Growth)
- P/E (Forward) – 44.44 (Growth)
- Economic Moat: Wide (product, innovative)
- Palo Alto Network provides network security solutions. The company's solution offerings spread across network security, cloud-native application protection, security operations, and endpoint security and are available across multiple key industries.
- Cybersecurity has 5 stage lifecycle - Identify, Protect, Detect, Recover and Restore. This cyclical process is essential for protecting an organisation from cyber threats. It helps to ensure that corporations are constantly prepared and able to respond to evolving threats.
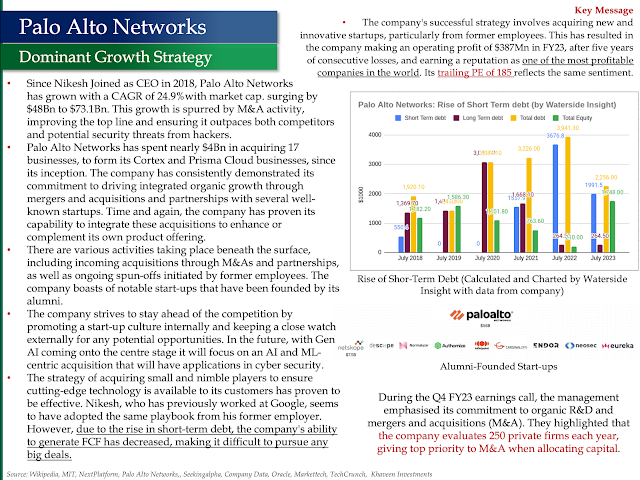
Dominating Growth Strategy
Since Nikesh Joined as CEO in 2018, Palo Alto Networks has grown with a CAGR of 24.9% with market cap. surging by $48Bn to $73.1Bn. This growth is spurred by M&A activity, improving the top line and ensuring it outpaces both competitors and potential security threats from hackers.
Palo Alto Networks has spent nearly $4Bn in acquiring 17 businesses, to form its Cortex and Prisma Cloud businesses, since its inception. The company has consistently demonstrated its commitment to driving integrated organic growth through mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships with several well-known startups. Time and again, the company has proven its capability to integrate these acquisitions to enhance or complement its own product offering.
There are various activities taking place beneath the surface, including incoming acquisitions through M&As and partnerships, as well as ongoing spin-offs initiated by former employees. The company boasts of notable start-ups that have been founded by its alumni.
The company strives to stay ahead of the competition by promoting a start-up culture internally and keeping a close watch externally for any potential opportunities. In the future, with Gen AI coming onto the centre stage it will focus on an AI and ML-centric acquisition that will have applications in cyber security.
The strategy of acquiring small and nimble players to ensure cutting-edge technology is available to its customers has proven effective. Nikesh, who has previously worked at Google, has adopted the same playbook from his former employer. However, due to the rise in short-term debt, the company's ability to generate FCF has decreased, making it difficult to pursue any big deals.
My other posts on Generative AI and Strategic Analysis of Key Players
- AI Value Chain
- Amazon the King of Retail -WhyAWS is the Crown Jewel
- Microsoft the King of AI in Software, Salesforce under the AI Cloud
- Tesla - It's not a Car, It's an AI Device on Wheels
- Google the King of Search - What the Future Beholds in the AI World
- Nvidia Godfather of AI - Why the Market is Bullish
- IBM - How it Lost Its Way
- Generative AI can transform Telecoms, Energy and Utilities
Monday, October 02, 2023
IBM a Tech Giant - How it Lost its Way
IBM a Tech Giant - How it Lost its Way
- Market Cap – $129.39Bn
- EV – $173.4Bn
- Debt - $57.5Bn, Cash - $17.9Bn
- P/B – 8.57
- P/E (Trailing) – 60.44 (Growth)
- P/E (Forward) – 14.3 (Div. Centric, No Growth)
- Economic Moat: Narrow (under threat)
Where is the Growth
How it Lost its Way
- IBM a more than 100-year-old company that used to be a trendsetter in the technology space has become a laggard and is struggling to get its Mojo back. It is facing headwinds, and it is not clear how it will modernise its business. Today, IBM has 3 business segments, Infrastructure, Software and Consulting, and all of them are declining YoY. There are multiple reasons why IBM's revenues are declining except for the minor surge in 2021, and 2022. Let's look at the key reasons.
- Unlike its peer group players like Salesforce and ServiceNow which specialises in providing packaged application software in the Cloud (SaaS), IBM has no application software to offer. Instead, IBM's software offering is primarily in system software, such as middleware, database management systems, and operating systems, that are used to build applications, but it has no end-user applications to offer. To add further, the issue with IBM's system software business is that it is increasingly moving towards open-source software, like how its other peer, Oracle is facing headwinds in the Database domain. IBM's Red Hat Enterprise Linux is built on open source and is cheaper than the company's legacy proprietary software.
- Microsoft, it's another peer, that competes with IBM in the Enterprise IT, has developed a mousetrap around Windows OS and its MS Office offering for both consumers and businesses. IBM, on the other hand, has no such product. Its other distant peer group players like Google and Meta, unlike IBM, earn most of its revenue from advertising.
- The IT spending in OPEX has been flat since the augment of Digital Transformation in the early 2010s. Most of the IT spending is CAPEX-centric for corporates to transform their businesses by rolling out customer-centric applications in the cloud and reducing the spending on system upgrades like Mainframes. In a way, the IT spending profile has significantly changed from being OPEX and IT-centric to CAPEX and business-driven. To add further, the Cloud first approach by businesses got a boost during the pandemic for resiliency and agility, ensuring that the likes of AWS and Microsoft extended their market share. In comparison, IBM has been relegated to a Cloud Consulting business where they help implement AWS, Azure and Google Cloud for their clients. This change is validated by IBM's Cloud market share decline from 25% in 2016 to 4% in 2022, indicating a lack of success in its effort to be a major player in this segment.
- IBM ventured into the AI industry during the early 2010s, introducing its Watson platform. However, the platform's performance was lacklustre, resulting in IBM selling its Watson Health initiative at a significant loss. The company is now making a fresh push into the market by relaunching Watson with the new name of watsonx, keeping in mind the current trend of Generation AI. IBM had previously rebranded its flagship database from DB2 to Db2 to rejuvenate it, but the move led to its downfall, especially among developers. IBM is now attempting a similar strategy with its AI offerings. It remains to be seen, whether rebranding will help IBM boost its AI efforts and achieve much-needed growth.
- During the mid-1990s, IBM decided to shift its focus from hardware manufacturing to the IT Managed Infrastructure Services sector, to drive growth in its software and consulting businesses by moving up the value chain. This strategic transition was necessary to meet the changing needs of customers who were moving away from mainframes and towards commodity hardware-enabled servers. However, in recent years, the IT Managed Infrastructure Services industry has experienced a decline due to the emergence of Hyperscalers and a change in IT spending. Today, most of IBM's original mainframe customers have shifted to the cloud or on-premise commodity hardware platforms for new application development, adding to the company's current challenge of finding ways to drive growth.
- IBM's IT Consulting segment has maintained a steady performance, with operating margins staying flat at 10-12%. The company has been pushed by market forces to shift its focus from providing consulting services solely based on its products to helping clients implement software from other companies. This shift is similar to the approach of a System Integrator. Despite IBM's attempt to emulate the cost arbitrage model of the leading Indian SI players, it has not been successful. Additionally, the margins in the consulting business have decreased, whereas the software business provides healthy margins due to the negligible marginal cost of selling an additional unit.
- To summarise, It's unsurprising that IBM is undervalued in comparison to its peers, given the various aspects that have been discussed. Wall Street analysts view IBM as a dividend stock with limited potential for capital growth, which is reflected in its forward PE of 14 and the market cap of $129Bn only, 18 times less than Microsoft's market cap of $2.4Tn.
My other posts on Generative AI and Strategic Analysis of Key Players
- AI Value Chain
- Amazon the King of Retail -WhyAWS is the Crown Jewel
- Microsoft the King of AI in Software, Salesforce under the AI Cloud
- Tesla - It's not a Car, It's an AI Device on Wheels
- Google the King of Search - What the Future Beholds in the AI World
- Nvidia Godfather of AI - Why the Market is Bullish
- Generative AI can transform Telecoms, Energy and Utilities
Sunday, October 01, 2023
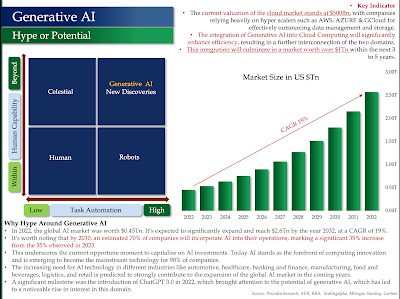
Generative AI - Changing the World, Key Players and Their Progress
Generative AI - Changing the World, Key Players and Their Progress - Part One
Singularity - Humanity on the Cusp of Achieving It?
What is Singularity?
A singularity is a theoretical condition that could arrive in the near future when a synthesis of several powerful new technologies will radically change the realities in which we find ourselves in an unpredictable manner.- Genetics (Bio-Technology)
- Nanotechnology
- Artificial intelligence AI
- Google's Bard, Gemini, BERT and T5
- Metas RoBERTa and XLM-R
- Tesla's Dojo enabled FSD
- Microsoft's and Open AI's, ChatGPT 4 enabled Bing and Co-Pilot
- XiaoIce and MT-DNN
- Amazon's Alexa, and Bedrock
- Apple's Siri
- IBM's Watson Assistant and Project Debater
- Rasa
- Hugging Face
- NVIDIA's Megatron and Triton
- SalesForce's Einstein
- SAP's Conversational AI
- DALL.E3: Creates realistic images and art from a description in natural language
- FaceApp: The app generates highly realistic transformations of the human face
- Talk To Books: You type a query or statement in the search box, and it discovers books related to that query
- Magic Eraser: It allows you to remove any unwanted objects from your photo while extending the background
- Replika: Allows you to create an AI personality and build a relationship with it
- Elsa: Analyzes speech and acts as an English-speaking coach
- Socratic: Helps students with their homework by providing educational resources
- Character.AI: Users can create characters, including their personalities, and publish them to the community for others to interact with
- Point E: Generates a 3D image based on the text written
- Youper: Helps users deal with emotional struggles by presenting them with different psychological techniques
- Manufacturing (Tesla)
- Healthcare Exploration and Science
- Mining
- Education
- Entertainment M
- Military and Security and many more domains
- Advancing our understanding of genetics
- Identifying genetic predispositions
- Personalised medicine
- Advancing drug development, specifically, gene therapy
- Improving diagnostic accuracy
Another benefit of mRNA technology is that it can be used to develop vaccines and therapeutics for a wide range of diseases. These vaccines are already being used to protect against COVID-19, and therapeutics are being developed to treat cancer, infectious diseases, and other conditions.
- COVID-19 vaccines: The Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines are both mRNA vaccines. These vaccines have been shown to be very safe and effective at preventing serious illness, hospitalisation, and death from COVID-19.
- Cancer vaccines: mRNA vaccines are being developed to treat a variety of cancers, including melanoma, lung cancer, and pancreatic cancer. These vaccines work by teaching the immune system to recognise and attack cancer cells.
- Infectious disease vaccines: mRNA vaccines are also being developed to protect against other infectious diseases, such as HIV, malaria, and Zika virus.
- Therapeutic vaccines: mRNA vaccines are being developed to treat a variety of conditions, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and multiple sclerosis. These vaccines work by teaching the immune system to repair damaged cells or to remove harmful substances from the body.
- Treating sickle cell anemia
- Preventing cancer, CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing has been used to prevent cancer in mice. In a study, researchers used CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing to disable a gene that is involved in cancer development. The mice that received the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing treatment were less likely to develop cancer than the mice that did not receive the treatment.
- Improving crop yields
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter on an atomic and molecular scale. It is a rapidly developing field with a wide range of potential applications in many different industries. Nanotechnology is already being used in a variety of industries, including:
- Healthcare: Nanotechnology is being used to develop new drugs and therapies, diagnostic tools, and medical devices. For example, nanoparticles can be used to deliver drugs directly to diseased cells, which can improve the effectiveness of the drugs and reduce side effects. Electronics: Nanotechnology is being used to develop new electronic devices that are smaller, faster, and more efficient than current devices. For example, carbon nanotubes can be used to make transistors that are much smaller and faster than silicon transistors.
- Energy: Nanotechnology is being used to develop new energy sources and storage devices. For example, nanomaterials can be used to make solar cells that are more efficient and less expensive than current solar cells.
- Environmental science: Nanotechnology is being used to develop new ways to clean up pollution and protect the environment. For example, nanomaterials can be used to remove pollutants from water and air.
- Food and agriculture: Nanotechnology is being used to develop new ways to produce and process food, and to improve the nutritional value of food. For example, nanomaterials can be used to make food packaging that is more effective at preserving food and preventing foodborne illness.
Here are some specific examples of how nanotechnology is being used in different industries:
- Healthcare:
- Nanoparticles are being used to deliver drugs directly to cancer cells, which can improve the effectiveness of the drugs and reduce side effects.
- Nanotechnology is being used to develop new diagnostic tools, such as blood tests that can detect cancer and other diseases early on.
- Nanotechnology is being used to develop new medical devices, such as artificial implants that are more durable and less likely to be rejected by the body.
- Electronics:
- Carbon nanotubes are being used to make transistors that are much smaller and faster than silicon transistors. Today TSMC has made a 3nm chip and is working on 2nm.
- Nanotechnology is being used to develop new types of batteries that are more efficient and have a longer lifespan than current batteries.
- Nanotechnology is being used to develop new types of displays that are brighter, more energy-efficient, and have higher resolution than current displays.
- Energy:
- Nanomaterials are being used to make solar cells that are more efficient and less expensive than current solar cells.
- Nanotechnology is being used to develop new types of fuel cells that are more efficient and produce less pollution than current fuel cells.
- Nanotechnology is being used to develop new types of batteries that can store more energy than current batteries.
- It is used in plasma-based tools in the recovery of oil and gas. These plasma processes are also used in additive manufacturing and 3D printing
- Environmental science:
- Nanomaterials are being used to remove pollutants from water and air.
- Nanotechnology is being used to develop new ways to clean up oil spills and other environmental disasters.
- Nanotechnology is being used to develop new ways to reduce the environmental impact of industrial processes.
- Food and agriculture:
- Nanomaterials are being used to make food packaging that is more effective at preserving food and preventing foodborne illness.
- Nanotechnology is being used to develop new ways to produce and process food, such as using nanomaterials to deliver nutrients to crops.
- Nanotechnology is being used to develop new ways to improve the nutritional value of food, such as using nanomaterials to encapsulate vitamins and minerals so that they are better absorbed by the body.
My other posts on similar topics like Generative AI and Strategic Analysis of Key Players
- AI Value Chain
- Amazon the King of Retail -WhyAWS is the Crown Jewel
- Microsoft the King of AI in Software, Salesforce under the AI Cloud
- Tesla - It's not a Car, It's an AI Device on Wheels
- Google the King of Search - What the Future Beholds in the AI World
- Nvidia Godfather of AI - Why the Market is Bullish
- IBM - How it Lost Its Way
- Generative AI can transform Telecoms, Energy and Utilities
Saturday, September 30, 2023
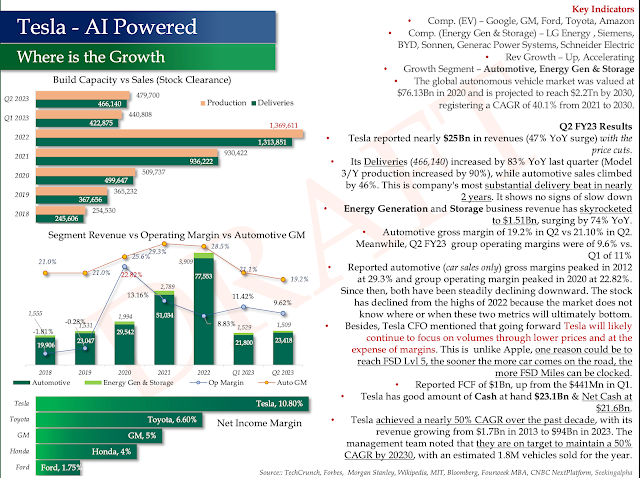
Tesla - Its not a Car, Its an AI Device on Wheels
Tesla - Evolution
Tesla's Secret of Success
Tesla - Where is the Growth
- AI Value Chain
- Amazon the King of Retail -WhyAWS is the Crown Jewel
- Microsoft the King of AI in Software, Salesforce under the AI Cloud
- Google the King of Search - What the Future Beholds in the AI World
- Taiwan Semiconductor - The Chipmaker That Runs The World
- Nvidia Godfather of AI - Why the Market is Bullish
- Generative AI can transform Telecoms, Energy and Utilities
Friday, September 29, 2023
Taiwan Semiconductor - The Chipmaker That Runs The World
Taiwan Semiconductor (TSMC) - The Chipmaker That Runs The World
Key Indicators
- Domain: Semiconductors
- Comp. (Chip Manf) – Samsung, SMIC, GFS, UMC
- Growth Segment – HPC AI Chips (Up)
- Economic Moat – Wide
- Cyclical - Yes
- TSMC's revenue is made up of 26% from Apple and 7% from Nvidia. Apple has a 10-year partnership with the chip maker.
- Apple designs chips for iPhones and Mac computers, while Google designs Tensor Chips for Pixel smartphones. Qualcomm and MediaTek design processors for Android phones. Nvidia designs Gaming and Artificial Intelligence (AI) processors, and AMD and Nvidia design advanced processors for Tesla.
- TSMC chips are also used by major cloud providers like AWS, MSFT, Google, Oracle, and IBM for data centres, networking, and software. Broadcom designs chips for broadband and wireless markets.
Generative Artificial Intelligence (Gen - AI)
training data.
Various types of Gen AI chips are
- GPU (Graphics Processing Unit)
- TPU (Tensor Processing Unit)
- FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array)
- ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit)
- Neuromorphic Chips
- AI Value Chain
- Amazon the King of Retail -WhyAWS is the Crown Jewel
- Microsoft the King of AI in Software, Salesforce under the AI Cloud
- Tesla - It's not a Car, Its an AI Device on Wheels
- Google the King of Search - What the Future Beholds in the AI World
- Nvidia Godfather of AI - Why the Market is Bullish
- Generative AI can transform Telecoms, Energy and Utilities