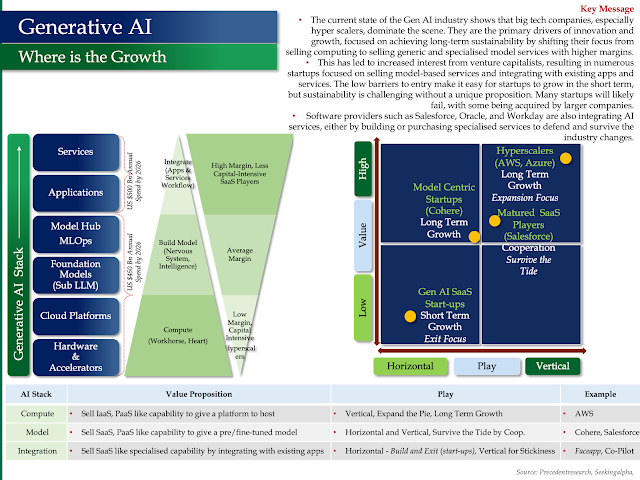
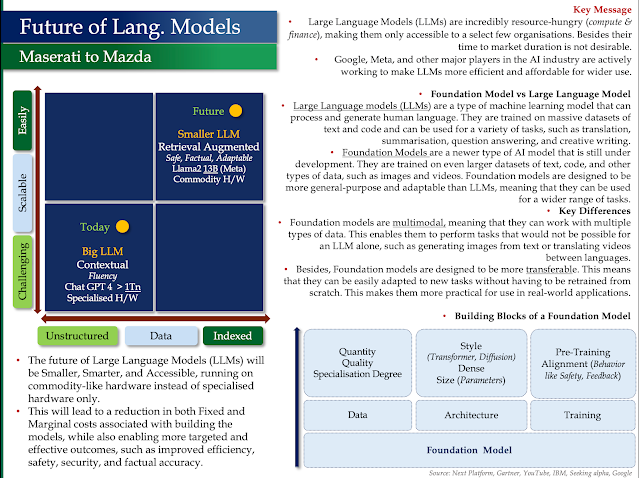
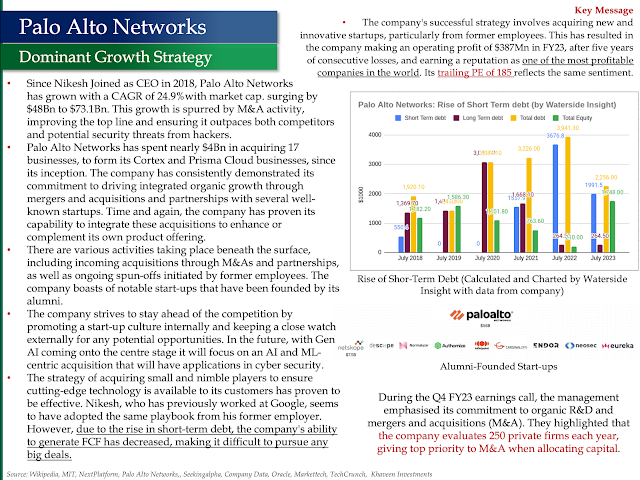
Let's break down how Snowflake, Palantir, and Databricks work together in the AI world, using a technology stack analogy and real-world examples.
The AI Technology Stack
Think of building an AI-powered company like building a house. You need a solid foundation, a smart design, and skilled builders.
-
Foundation (Data): Snowflake
- Layman's Terms: Snowflake is like the concrete foundation of your AI house. It stores all your data in one organised place, making it easy to access and use.
It's not just storage; it's like a super-organised library where any information can be found instantly. - Technical Function: Snowflake is a cloud-based data warehouse.
It allows companies to store vast amounts of structured and semi-structured data, making it readily available for analysis and AI model training. It handles the messy work of data organisation and access. - Example: Imagine a retail company. Snowflake stores all its sales data, customer information, inventory levels, and even website traffic data. Because it's all in one place and easily accessible, the company can quickly analyse what products are selling well, who their best customers are, and how to optimise their inventory.
- Layman's Terms: Snowflake is like the concrete foundation of your AI house. It stores all your data in one organised place, making it easy to access and use.
-
Design (Intelligence): Palantir
- Layman's Terms: Palantir is like the architect of your AI house. It takes the data from Snowflake and uses it to design intelligent systems. It helps you understand what the data means and how to use it to make better decisions. It's like turning raw data into actionable insights.
- Technical Function: Palantir is an operational platform that connects data, analytics, and operations.
It uses AI to analyse data from Snowflake (and other sources) and create visualisations, dashboards, and predictive models that help businesses make better decisions. It focuses on turning data into action. - Example: Using the retail company example, Palantir can take the data from Snowflake and build a model that predicts which customers are most likely to buy a certain product. It can then automate marketing campaigns to target those customers, increasing sales.
Or, it can analyse supply chain data to predict potential disruptions and suggest alternative suppliers.
-
Builders (AI Development): Databricks
- Layman's Terms: Databricks is like the construction crew for your AI house. They use the data from Snowflake and the designs from Palantir to build and maintain the actual AI systems. They're the experts who know how to put everything together. They keep the AI models up-to-date and running smoothly.
- Technical Function: Databricks provides a unified analytics platform for data science and machine learning.
It allows data scientists to build, train, and deploy AI models at scale. It offers tools for data engineering, model development, and MLOps (machine learning operations). - Example: For our retail company, Databricks would be used to build and train the AI model that predicts customer behaviour. They would use the data in Snowflake and work with the insights provided by Palantir to create a model that is accurate and effective. They would also manage the ongoing maintenance and updates to that model.
Diagram of the Stack
+-----------------+
| Applications | (e.g., Marketing automation, Supply chain optimization)
+-----------------+
| Palantir | (Intelligence Layer - AI-driven decision making)
+-----------------+
| Snowflake | (Data Layer - Unified data storage and access)
+-----------------+
| Databricks | (AI Development Layer - Model building, training, deployment)
+-----------------+
Example Flow
- The retail company stores all its data (sales, customers, inventory, etc.) in Snowflake.
- Databricks uses this data to build an AI model that predicts which customers are likely to buy a new product.
- Palantir takes the output of this model and uses it to create targeted marketing campaigns.
- The results of these campaigns (new sales, customer engagement) are then stored back in Snowflake, and the process begins again, allowing the AI models to continuously learn and improve.
In short, Snowflake provides the data, Palantir provides the intelligence, and Databricks provides the tools to build and deploy the AI systems that drive the AI-native enterprise. They are the essential components for companies looking to leverage AI effectively